This widget produces an actual window. More...
#include <Fl_Window.H>
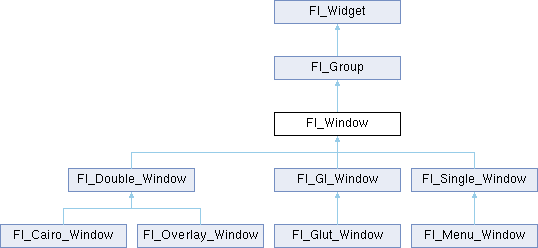
Classes | |
| struct | shape_data_type |
| Data supporting a non-rectangular window shape. More... | |
Public Member Functions | |
| virtual Fl_Window * | as_window () |
| Returns an Fl_Window pointer if this widget is an Fl_Window. | |
| unsigned int | border () const |
| See void Fl_Window::border(int) | |
| void | border (int b) |
| Sets whether or not the window manager border is around the window. | |
| void | clear_border () |
| Fast inline function to turn the window manager border off. | |
| void | clear_modal_states () |
| Clears the "modal" flags and converts a "modal" or "non-modal" window back into a "normal" window. | |
| void | copy_label (const char *a) |
| Sets the window titlebar label to a copy of a character string. | |
| void | cursor (const Fl_RGB_Image *, int, int) |
| Changes the cursor for this window. | |
| void | cursor (Fl_Cursor c, Fl_Color, Fl_Color=FL_WHITE) |
| For back compatibility only. | |
| void | cursor (Fl_Cursor) |
| Changes the cursor for this window. | |
| int | decorated_h () |
| Returns the window height including any window title bar and any frame added by the window manager. | |
| int | decorated_w () |
| Returns the window width including any frame added by the window manager. | |
| void | default_cursor (Fl_Cursor c, Fl_Color, Fl_Color=FL_WHITE) |
| For back compatibility only. | |
| void | default_cursor (Fl_Cursor) |
| Sets the default window cursor. | |
| Fl_Window (int w, int h, const char *title=0) | |
| Creates a window from the given size and title. | |
| Fl_Window (int x, int y, int w, int h, const char *title=0) | |
| Creates a window from the given position, size and title. | |
| void | free_position () |
| Undoes the effect of a previous resize() or show() so that the next time show() is called the window manager is free to position the window. | |
| void | fullscreen () |
| Makes the window completely fill one or more screens, without any window manager border visible. | |
| unsigned int | fullscreen_active () const |
| Returns non zero if FULLSCREEN flag is set, 0 otherwise. | |
| void | fullscreen_off () |
| Turns off any side effects of fullscreen() | |
| void | fullscreen_off (int X, int Y, int W, int H) |
| Turns off any side effects of fullscreen() and does resize(x,y,w,h). | |
| void | fullscreen_screens (int top, int bottom, int left, int right) |
| Sets which screens should be used when this window is in fullscreen mode. | |
| virtual int | handle (int) |
| Handles the specified event. | |
| virtual void | hide () |
| Removes the window from the screen. | |
| void | hotspot (const Fl_Widget &p, int offscreen=0) |
| See void Fl_Window::hotspot(int x, int y, int offscreen = 0) | |
| void | hotspot (const Fl_Widget *, int offscreen=0) |
| See void Fl_Window::hotspot(int x, int y, int offscreen = 0) | |
| void | hotspot (int x, int y, int offscreen=0) |
| Positions the window so that the mouse is pointing at the given position, or at the center of the given widget, which may be the window itself. | |
| const void * | icon () const |
| Gets the current icon window target dependent data. | |
| void | icon (const Fl_RGB_Image *) |
| Sets or resets a single window icon. | |
| void | icon (const void *ic) |
| Sets the current icon window target dependent data. | |
| void | iconize () |
| Iconifies the window. | |
| const char * | iconlabel () const |
| See void Fl_Window::iconlabel(const char*) | |
| void | iconlabel (const char *) |
| Sets the icon label. | |
| void | icons (const Fl_RGB_Image *[], int) |
| Sets the window icons. | |
| const char * | label () const |
| See void Fl_Window::label(const char*) | |
| void | label (const char *) |
| Sets the window title bar label. | |
| void | label (const char *label, const char *iconlabel) |
| Sets the icon label. | |
| void | make_current () |
| Sets things up so that the drawing functions in <FL/fl_draw.H> will go into this window. | |
| unsigned int | menu_window () const |
| Returns true if this window is a menu window. | |
| unsigned int | modal () const |
| Returns true if this window is modal. | |
| unsigned int | non_modal () const |
| Returns true if this window is modal or non-modal. | |
| unsigned int | override () const |
| Returns non zero if FL_OVERRIDE flag is set, 0 otherwise. | |
| virtual void | resize (int X, int Y, int W, int H) |
| Changes the size and position of the window. | |
| void | set_menu_window () |
| Marks the window as a menu window. | |
| void | set_modal () |
| A "modal" window, when shown(), will prevent any events from being delivered to other windows in the same program, and will also remain on top of the other windows (if the X window manager supports the "transient for" property). | |
| void | set_non_modal () |
| A "non-modal" window (terminology borrowed from Microsoft Windows) acts like a modal() one in that it remains on top, but it has no effect on event delivery. | |
| void | set_override () |
| Activates the flags NOBORDER|FL_OVERRIDE. | |
| void | set_tooltip_window () |
| Marks the window as a tooltip window. | |
| void | shape (const Fl_Image &b) |
| Set the window's shape with an Fl_Image. | |
| void | shape (const Fl_Image *img) |
| Assigns a non-rectangular shape to the window. | |
| virtual void | show () |
| Puts the window on the screen. | |
| void | show (int argc, char **argv) |
| Puts the window on the screen and parses command-line arguments. | |
| int | shown () |
| Returns non-zero if show() has been called (but not hide() ). | |
| void | size_range (int minw, int minh, int maxw=0, int maxh=0, int dw=0, int dh=0, int aspect=0) |
| Sets the allowable range the user can resize this window to. | |
| unsigned int | tooltip_window () const |
| Returns true if this window is a tooltip window. | |
| void | wait_for_expose () |
| Waits for the window to be displayed after calling show(). | |
| int | x_root () const |
| Gets the x position of the window on the screen. | |
| const char * | xclass () const |
| Returns the xclass for this window, or a default. | |
| void | xclass (const char *c) |
| Sets the xclass for this window. | |
| int | y_root () const |
| Gets the y position of the window on the screen. | |
| virtual | ~Fl_Window () |
| The destructor also deletes all the children. | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from Fl_Group Public Member Functions inherited from Fl_Group | |
| Fl_Widget *& | _ddfdesign_kludge () |
| This is for forms compatibility only. | |
| void | add (Fl_Widget &) |
| The widget is removed from its current group (if any) and then added to the end of this group. | |
| void | add (Fl_Widget *o) |
| See void Fl_Group::add(Fl_Widget &w) | |
| void | add_resizable (Fl_Widget &o) |
| Adds a widget to the group and makes it the resizable widget. | |
| Fl_Widget *const * | array () const |
| Returns a pointer to the array of children. | |
| virtual Fl_Group * | as_group () |
| Returns an Fl_Group pointer if this widget is an Fl_Group. | |
| void | begin () |
| Sets the current group so you can build the widget tree by just constructing the widgets. | |
| Fl_Widget * | child (int n) const |
| Returns array()[n]. | |
| int | children () const |
| Returns how many child widgets the group has. | |
| void | clear () |
| Deletes all child widgets from memory recursively. | |
| unsigned int | clip_children () |
| Returns the current clipping mode. | |
| void | clip_children (int c) |
| Controls whether the group widget clips the drawing of child widgets to its bounding box. | |
| void | end () |
| Exactly the same as current(this->parent()). | |
| int | find (const Fl_Widget &o) const |
| See int Fl_Group::find(const Fl_Widget *w) const. | |
| int | find (const Fl_Widget *) const |
| Searches the child array for the widget and returns the index. | |
| Fl_Group (int, int, int, int, const char *=0) | |
| Creates a new Fl_Group widget using the given position, size, and label string. | |
| void | focus (Fl_Widget *W) |
| void | forms_end () |
| This is for forms compatibility only. | |
| void | init_sizes () |
| Resets the internal array of widget sizes and positions. | |
| void | insert (Fl_Widget &, int i) |
| The widget is removed from its current group (if any) and then inserted into this group. | |
| void | insert (Fl_Widget &o, Fl_Widget *before) |
| This does insert(w, find(before)). | |
| void | remove (Fl_Widget &) |
| Removes a widget from the group but does not delete it. | |
| void | remove (Fl_Widget *o) |
Removes the widget o from the group. | |
| void | remove (int index) |
Removes the widget at index from the group but does not delete it. | |
| Fl_Widget * | resizable () const |
| See void Fl_Group::resizable(Fl_Widget *box) | |
| void | resizable (Fl_Widget &o) |
| See void Fl_Group::resizable(Fl_Widget *box) | |
| void | resizable (Fl_Widget *o) |
| The resizable widget defines the resizing box for the group. | |
| virtual | ~Fl_Group () |
| The destructor also deletes all the children. | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from Fl_Widget Public Member Functions inherited from Fl_Widget | |
| void | _clear_fullscreen () |
| void | _set_fullscreen () |
| void | activate () |
| Activates the widget. | |
| unsigned int | active () const |
| Returns whether the widget is active. | |
| int | active_r () const |
| Returns whether the widget and all of its parents are active. | |
| Fl_Align | align () const |
| Gets the label alignment. | |
| void | align (Fl_Align alignment) |
| Sets the label alignment. | |
| long | argument () const |
| Gets the current user data (long) argument that is passed to the callback function. | |
| void | argument (long v) |
| Sets the current user data (long) argument that is passed to the callback function. | |
| virtual class Fl_Gl_Window * | as_gl_window () |
| Returns an Fl_Gl_Window pointer if this widget is an Fl_Gl_Window. | |
| Fl_Boxtype | box () const |
| Gets the box type of the widget. | |
| void | box (Fl_Boxtype new_box) |
| Sets the box type for the widget. | |
| Fl_Callback_p | callback () const |
| Gets the current callback function for the widget. | |
| void | callback (Fl_Callback *cb) |
| Sets the current callback function for the widget. | |
| void | callback (Fl_Callback *cb, void *p) |
| Sets the current callback function for the widget. | |
| void | callback (Fl_Callback0 *cb) |
| Sets the current callback function for the widget. | |
| void | callback (Fl_Callback1 *cb, long p=0) |
| Sets the current callback function for the widget. | |
| unsigned int | changed () const |
| Checks if the widget value changed since the last callback. | |
| void | clear_active () |
| Marks the widget as inactive without sending events or changing focus. | |
| void | clear_changed () |
| Marks the value of the widget as unchanged. | |
| void | clear_damage (uchar c=0) |
| Clears or sets the damage flags. | |
| void | clear_output () |
| Sets a widget to accept input. | |
| void | clear_visible () |
| Hides the widget. | |
| void | clear_visible_focus () |
| Disables keyboard focus navigation with this widget. | |
| Fl_Color | color () const |
| Gets the background color of the widget. | |
| void | color (Fl_Color bg) |
| Sets the background color of the widget. | |
| void | color (Fl_Color bg, Fl_Color sel) |
| Sets the background and selection color of the widget. | |
| Fl_Color | color2 () const |
| For back compatibility only. | |
| void | color2 (unsigned a) |
| For back compatibility only. | |
| int | contains (const Fl_Widget *w) const |
| Checks if w is a child of this widget. | |
| void | copy_label (const char *new_label) |
| Sets the current label. | |
| void | copy_tooltip (const char *text) |
| Sets the current tooltip text. | |
| uchar | damage () const |
| Returns non-zero if draw() needs to be called. | |
| void | damage (uchar c) |
| Sets the damage bits for the widget. | |
| void | damage (uchar c, int x, int y, int w, int h) |
| Sets the damage bits for an area inside the widget. | |
| int | damage_resize (int, int, int, int) |
| Internal use only. | |
| void | deactivate () |
| Deactivates the widget. | |
| Fl_Image * | deimage () |
| Gets the image that is used as part of the widget label. | |
| const Fl_Image * | deimage () const |
| void | deimage (Fl_Image &img) |
| Sets the image to use as part of the widget label. | |
| void | deimage (Fl_Image *img) |
| Sets the image to use as part of the widget label. | |
| void | do_callback () |
| Calls the widget callback. | |
| void | do_callback (Fl_Widget *o, long arg) |
| Calls the widget callback. | |
| void | do_callback (Fl_Widget *o, void *arg=0) |
| Calls the widget callback. | |
| void | draw_label (int, int, int, int, Fl_Align) const |
| Draws the label in an arbitrary bounding box with an arbitrary alignment. | |
| int | h () const |
| Gets the widget height. | |
| Fl_Image * | image () |
| Gets the image that is used as part of the widget label. | |
| const Fl_Image * | image () const |
| void | image (Fl_Image &img) |
| Sets the image to use as part of the widget label. | |
| void | image (Fl_Image *img) |
| Sets the image to use as part of the widget label. | |
| int | inside (const Fl_Widget *wgt) const |
Checks if this widget is a child of wgt. | |
| int | is_label_copied () const |
| Returns whether the current label was assigned with copy_label(). | |
| const char * | label () const |
| Gets the current label text. | |
| void | label (const char *text) |
| Sets the current label pointer. | |
| void | label (Fl_Labeltype a, const char *b) |
| Shortcut to set the label text and type in one call. | |
| Fl_Color | labelcolor () const |
| Gets the label color. | |
| void | labelcolor (Fl_Color c) |
| Sets the label color. | |
| Fl_Font | labelfont () const |
| Gets the font to use. | |
| void | labelfont (Fl_Font f) |
| Sets the font to use. | |
| Fl_Fontsize | labelsize () const |
| Gets the font size in pixels. | |
| void | labelsize (Fl_Fontsize pix) |
| Sets the font size in pixels. | |
| Fl_Labeltype | labeltype () const |
| Gets the label type. | |
| void | labeltype (Fl_Labeltype a) |
| Sets the label type. | |
| void | measure_label (int &ww, int &hh) const |
| Sets width ww and height hh accordingly with the label size. | |
| unsigned int | output () const |
| Returns if a widget is used for output only. | |
| Fl_Group * | parent () const |
| Returns a pointer to the parent widget. | |
| void | parent (Fl_Group *p) |
| Internal use only - "for hacks only". | |
| void | position (int X, int Y) |
| Repositions the window or widget. | |
| void | redraw () |
| Schedules the drawing of the widget. | |
| void | redraw_label () |
| Schedules the drawing of the label. | |
| Fl_Color | selection_color () const |
| Gets the selection color. | |
| void | selection_color (Fl_Color a) |
| Sets the selection color. | |
| void | set_active () |
| Marks the widget as active without sending events or changing focus. | |
| void | set_changed () |
| Marks the value of the widget as changed. | |
| void | set_output () |
| Sets a widget to output only. | |
| void | set_visible () |
| Makes the widget visible. | |
| void | set_visible_focus () |
| Enables keyboard focus navigation with this widget. | |
| void | size (int W, int H) |
| Changes the size of the widget. | |
| int | take_focus () |
| Gives the widget the keyboard focus. | |
| unsigned int | takesevents () const |
| Returns if the widget is able to take events. | |
| int | test_shortcut () |
| Returns true if the widget's label contains the entered '&x' shortcut. | |
| const char * | tooltip () const |
| Gets the current tooltip text. | |
| void | tooltip (const char *text) |
| Sets the current tooltip text. | |
| Fl_Window * | top_window () const |
| Returns a pointer to the top-level window for the widget. | |
| Fl_Window * | top_window_offset (int &xoff, int &yoff) const |
| Finds the x/y offset of the current widget relative to the top-level window. | |
| uchar | type () const |
| Gets the widget type. | |
| void | type (uchar t) |
| Sets the widget type. | |
| int | use_accents_menu () |
| Returns non zero if MAC_USE_ACCENTS_MENU flag is set, 0 otherwise. | |
| void * | user_data () const |
| Gets the user data for this widget. | |
| void | user_data (void *v) |
| Sets the user data for this widget. | |
| unsigned int | visible () const |
| Returns whether a widget is visible. | |
| unsigned int | visible_focus () |
| Checks whether this widget has a visible focus. | |
| void | visible_focus (int v) |
| Modifies keyboard focus navigation. | |
| int | visible_r () const |
| Returns whether a widget and all its parents are visible. | |
| int | w () const |
| Gets the widget width. | |
| Fl_When | when () const |
| Returns the conditions under which the callback is called. | |
| void | when (uchar i) |
| Sets the flags used to decide when a callback is called. | |
| Fl_Window * | window () const |
| Returns a pointer to the nearest parent window up the widget hierarchy. | |
| int | x () const |
| Gets the widget position in its window. | |
| int | y () const |
| Gets the widget position in its window. | |
| virtual | ~Fl_Widget () |
| Destroys the widget. | |
Static Public Member Functions | |
| static Fl_Window * | current () |
| Returns the last window that was made current. | |
| static void | default_callback (Fl_Window *, void *v) |
| Back compatibility: Sets the default callback v for win to call on close event. | |
| static void | default_icon (const Fl_RGB_Image *) |
| Sets a single default window icon. | |
| static void | default_icons (const Fl_RGB_Image *[], int) |
| Sets the default window icons. | |
| static const char * | default_xclass () |
| Returns the default xclass. | |
| static void | default_xclass (const char *) |
| Sets the default window xclass. | |
 Static Public Member Functions inherited from Fl_Group Static Public Member Functions inherited from Fl_Group | |
| static Fl_Group * | current () |
| Returns the currently active group. | |
| static void | current (Fl_Group *g) |
| Sets the current group. | |
 Static Public Member Functions inherited from Fl_Widget Static Public Member Functions inherited from Fl_Widget | |
| static void | default_callback (Fl_Widget *cb, void *d) |
| The default callback for all widgets that don't set a callback. | |
| static unsigned int | label_shortcut (const char *t) |
| Returns the Unicode value of the '&x' shortcut in a given text. | |
| static int | test_shortcut (const char *, const bool require_alt=false) |
Returns true if the given text t contains the entered '&x' shortcut. | |
Protected Member Functions | |
| virtual void | draw () |
| Draws the widget. | |
| virtual void | flush () |
| Forces the window to be drawn, this window is also made current and calls draw(). | |
| int | force_position () const |
| Returns the internal state of the window's FORCE_POSITION flag. | |
| void | force_position (int force) |
| Sets an internal flag that tells FLTK and the window manager to honor position requests. | |
| void | free_icons () |
| Deletes all icons previously attached to the window. | |
 Protected Member Functions inherited from Fl_Group Protected Member Functions inherited from Fl_Group | |
| void | draw_child (Fl_Widget &widget) const |
| Forces a child to redraw. | |
| void | draw_children () |
| Draws all children of the group. | |
| void | draw_outside_label (const Fl_Widget &widget) const |
| Parents normally call this to draw outside labels of child widgets. | |
| int * | sizes () |
| Returns the internal array of widget sizes and positions. | |
| void | update_child (Fl_Widget &widget) const |
| Draws a child only if it needs it. | |
 Protected Member Functions inherited from Fl_Widget Protected Member Functions inherited from Fl_Widget | |
| void | clear_flag (unsigned int c) |
| Clears a flag in the flags mask. | |
| void | draw_backdrop () const |
| If FL_ALIGN_IMAGE_BACKDROP is set, the image or deimage will be drawn. | |
| void | draw_box () const |
| Draws the widget box according its box style. | |
| void | draw_box (Fl_Boxtype t, Fl_Color c) const |
| Draws a box of type t, of color c at the widget's position and size. | |
| void | draw_box (Fl_Boxtype t, int x, int y, int w, int h, Fl_Color c) const |
| Draws a box of type t, of color c at the position X,Y and size W,H. | |
| void | draw_focus () |
| draws a focus rectangle around the widget | |
| void | draw_focus (Fl_Boxtype t, int x, int y, int w, int h) const |
| Draws a focus box for the widget at the given position and size. | |
| void | draw_label () const |
| Draws the widget's label at the defined label position. | |
| void | draw_label (int, int, int, int) const |
| Draws the label in an arbitrary bounding box. | |
| Fl_Widget (int x, int y, int w, int h, const char *label=0L) | |
| Creates a widget at the given position and size. | |
| unsigned int | flags () const |
| Gets the widget flags mask. | |
| void | h (int v) |
| Internal use only. | |
| void | set_flag (unsigned int c) |
| Sets a flag in the flags mask. | |
| void | w (int v) |
| Internal use only. | |
| void | x (int v) |
| Internal use only. | |
| void | y (int v) |
| Internal use only. | |
Protected Attributes | |
| shape_data_type * | shape_data_ |
| non-null means the window has a non-rectangular shape | |
Static Protected Attributes | |
| static Fl_Window * | current_ |
| Stores the last window that was made current. | |
Friends | |
| class | Fl_X |
Additional Inherited Members | |
 Protected Types inherited from Fl_Widget Protected Types inherited from Fl_Widget | |
| enum | { INACTIVE = 1<<0 , INVISIBLE = 1<<1 , OUTPUT = 1<<2 , NOBORDER = 1<<3 , FORCE_POSITION = 1<<4 , NON_MODAL = 1<<5 , SHORTCUT_LABEL = 1<<6 , CHANGED = 1<<7 , OVERRIDE = 1<<8 , VISIBLE_FOCUS = 1<<9 , COPIED_LABEL = 1<<10 , CLIP_CHILDREN = 1<<11 , MENU_WINDOW = 1<<12 , TOOLTIP_WINDOW = 1<<13 , MODAL = 1<<14 , NO_OVERLAY = 1<<15 , GROUP_RELATIVE = 1<<16 , COPIED_TOOLTIP = 1<<17 , FULLSCREEN = 1<<18 , MAC_USE_ACCENTS_MENU = 1<<19 , USERFLAG3 = 1<<29 , USERFLAG2 = 1<<30 , USERFLAG1 = 1<<31 } |
| flags possible values enumeration. More... | |
Detailed Description
This widget produces an actual window.
This can either be a main window, with a border and title and all the window management controls, or a "subwindow" inside a window. This is controlled by whether or not the window has a parent().
Once you create a window, you usually add children Fl_Widget 's to it by using window->add(child) for each new widget. See Fl_Group for more information on how to add and remove children.
There are several subclasses of Fl_Window that provide double-buffering, overlay, menu, and OpenGL support.
The window's callback is done if the user tries to close a window using the window manager and Fl::modal() is zero or equal to the window. Fl_Window has a default callback that calls Fl_Window::hide().
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
◆ Fl_Window() [1/2]
| Fl_Window::Fl_Window | ( | int | w, |
| int | h, | ||
| const char * | title = 0 ) |
Creates a window from the given size and title.
If Fl_Group::current() is not NULL, the window is created as a subwindow of the parent window.
The (w,h) form of the constructor creates a top-level window and asks the window manager to position the window. The (x,y,w,h) form of the constructor either creates a subwindow or a top-level window at the specified location (x,y) , subject to window manager configuration. If you do not specify the position of the window, the window manager will pick a place to show the window or allow the user to pick a location. Use position(x,y) or hotspot() before calling show() to request a position on the screen. See Fl_Window::resize() for some more details on positioning windows.
Top-level windows initially have visible() set to 0 and parent() set to NULL. Subwindows initially have visible() set to 1 and parent() set to the parent window pointer.
Fl_Widget::box() defaults to FL_FLAT_BOX. If you plan to completely fill the window with children widgets you should change this to FL_NO_BOX. If you turn the window border off you may want to change this to FL_UP_BOX.
◆ Fl_Window() [2/2]
| Fl_Window::Fl_Window | ( | int | x, |
| int | y, | ||
| int | w, | ||
| int | h, | ||
| const char * | title = 0 ) |
Creates a window from the given position, size and title.
◆ ~Fl_Window()
|
virtual |
The destructor also deletes all the children.
This allows a whole tree to be deleted at once, without having to keep a pointer to all the children in the user code. A kludge has been done so the Fl_Window and all of its children can be automatic (local) variables, but you must declare the Fl_Window first so that it is destroyed last.
Member Function Documentation
◆ as_window()
|
inlinevirtual |
Returns an Fl_Window pointer if this widget is an Fl_Window.
Use this method if you have a widget (pointer) and need to know whether this widget is derived from Fl_Window. If it returns non-NULL, then the widget in question is derived from Fl_Window, and you can use the returned pointer to access its children or other Fl_Window-specific methods.
- Return values
-
NULL if this widget is not derived from Fl_Window.
- Note
- This method is provided to avoid dynamic_cast.
Reimplemented from Fl_Widget.
◆ border()
| void Fl_Window::border | ( | int | b | ) |
Sets whether or not the window manager border is around the window.
The default value is true. void border(int) can be used to turn the border on and off. Under most X window managers this does not work after show() has been called, although SGI's 4DWM does work.
◆ clear_border()
|
inline |
Fast inline function to turn the window manager border off.
It only works before show() is called.
◆ clear_modal_states()
|
inline |
Clears the "modal" flags and converts a "modal" or "non-modal" window back into a "normal" window.
Note that there are three states for a window: modal, non-modal, and normal.
You can not change the "modality" of a window whilst it is shown, so it is necessary to first hide() the window, change its "modality" as required, then re-show the window for the new state to take effect.
This method can also be used to change a "modal" window into a "non-modal" one. On several supported platforms, the "modal" state over-rides the "non-modal" state, so the "modal" state must be cleared before the window can be set into the "non-modal" state. In general, the following sequence should work:
- Note
- Under some window managers, the sequence of hiding the window and changing its modality will often cause it to be re-displayed at a different position when it is subsequently shown. This is an irritating feature but appears to be unavoidable at present. As a result we would advise to use this method only when absolutely necessary.
- See also
- void set_modal(), void set_non_modal()
◆ current()
|
static |
Returns the last window that was made current.
- See also
- Fl_Window::make_current()
◆ cursor() [1/3]
| void Fl_Window::cursor | ( | const Fl_RGB_Image * | image, |
| int | hotx, | ||
| int | hoty ) |
Changes the cursor for this window.
This always calls the system, if you are changing the cursor a lot you may want to keep track of how you set it in a static variable and call this only if the new cursor is different.
The default cursor will be used if the provided image cannot be used as a cursor.
- See also
- cursor(Fl_Cursor), default_cursor()
◆ cursor() [2/3]
For back compatibility only.
Same as Fl_Window::cursor(Fl_Cursor)
◆ cursor() [3/3]
| void Fl_Window::cursor | ( | Fl_Cursor | c | ) |
Changes the cursor for this window.
This always calls the system, if you are changing the cursor a lot you may want to keep track of how you set it in a static variable and call this only if the new cursor is different.
The type Fl_Cursor is an enumeration defined in <FL/Enumerations.H>.
◆ decorated_h()
| int Fl_Window::decorated_h | ( | ) |
Returns the window height including any window title bar and any frame added by the window manager.
Same as h() if applied to a subwindow.
◆ decorated_w()
| int Fl_Window::decorated_w | ( | ) |
Returns the window width including any frame added by the window manager.
Same as w() if applied to a subwindow.
◆ default_cursor() [1/2]
For back compatibility only.
◆ default_cursor() [2/2]
| void Fl_Window::default_cursor | ( | Fl_Cursor | c | ) |
Sets the default window cursor.
This is the cursor that will be used after the mouse pointer leaves a widget with a custom cursor set.
◆ default_icon()
|
static |
Sets a single default window icon.
If icon is NULL the current default icons are removed.
- Parameters
-
[in] icon default icon for all windows subsequently created or NULL
◆ default_icons()
|
static |
Sets the default window icons.
The default icons are used for all windows that don't have their own icons set before show() is called. You can change the default icons whenever you want, but this only affects windows that are created (and shown) after this call.
The given images in icons are copied. You can use a local variable or free the images immediately after this call.
- Parameters
-
[in] icons default icons for all windows subsequently created [in] count number of images in icons. Set to 0 to remove the current default icons
◆ default_xclass() [1/2]
|
static |
Returns the default xclass.
◆ default_xclass() [2/2]
|
static |
Sets the default window xclass.
The default xclass is used for all windows that don't have their own xclass set before show() is called. You can change the default xclass whenever you want, but this only affects windows that are created (and shown) after this call.
The given string xc is copied. You can use a local variable or free the string immediately after this call.
If you don't call this, the default xclass for all windows will be "FLTK". You can reset the default xclass by specifying NULL for xc.
If you call Fl_Window::xclass(const char *) for any window, then this also sets the default xclass, unless it has been set before.
- Parameters
-
[in] xc default xclass for all windows subsequently created
- See also
- Fl_Window::xclass(const char *)
◆ draw()
|
protectedvirtual |
Draws the widget.
Never call this function directly. FLTK will schedule redrawing whenever needed. If your widget must be redrawn as soon as possible, call redraw() instead.
Override this function to draw your own widgets.
If you ever need to call another widget's draw method from within your own draw() method, e.g. for an embedded scrollbar, you can do it (because draw() is virtual) like this:
Reimplemented from Fl_Group.
Reimplemented in Fl_Cairo_Window, Fl_Gl_Window, and Fl_Glut_Window.
◆ flush()
|
protectedvirtual |
Forces the window to be drawn, this window is also made current and calls draw().
Reimplemented in Fl_Double_Window, Fl_Gl_Window, Fl_Menu_Window, Fl_Overlay_Window, and Fl_Single_Window.
◆ force_position() [1/2]
|
inlineprotected |
Returns the internal state of the window's FORCE_POSITION flag.
- Return values
-
1 if flag is set 0 otherwise
- See also
- force_position(int)
◆ force_position() [2/2]
|
inlineprotected |
Sets an internal flag that tells FLTK and the window manager to honor position requests.
This is used internally and should not be needed by user code.
- Parameters
-
[in] force 1 to set the FORCE_POSITION flag, 0 to clear it
◆ free_icons()
|
protected |
Deletes all icons previously attached to the window.
◆ free_position()
|
inline |
Undoes the effect of a previous resize() or show() so that the next time show() is called the window manager is free to position the window.
This is for Forms compatibility only.
- Deprecated
- please use force_position(0) instead
◆ fullscreen()
| void Fl_Window::fullscreen | ( | ) |
Makes the window completely fill one or more screens, without any window manager border visible.
You must use fullscreen_off() to undo this.
- Note
- On some platforms, this can result in the keyboard being grabbed. The window may also be recreated, meaning hide() and show() will be called.
- See also
- void Fl_Window::fullscreen_screens()
◆ fullscreen_screens()
| void Fl_Window::fullscreen_screens | ( | int | top, |
| int | bottom, | ||
| int | left, | ||
| int | right ) |
Sets which screens should be used when this window is in fullscreen mode.
The window will be resized to the top of the screen with index top, the bottom of the screen with index bottom, etc.
If this method is never called, or if any argument is < 0, then the window will be resized to fill the screen it is currently on.
- See also
- void Fl_Window::fullscreen()
◆ handle()
|
virtual |
Handles the specified event.
You normally don't call this method directly, but instead let FLTK do it when the user interacts with the widget.
When implemented in a widget, this function must return 0 if the widget does not use the event or 1 otherwise.
Most of the time, you want to call the inherited handle() method in your overridden method so that you don't short-circuit events that you don't handle. In this last case you should return the callee retval.
- Parameters
-
[in] event the kind of event received
- Return values
-
0 if the event was not used or understood 1 if the event was used and can be deleted
- See also
- Fl_Event
Reimplemented from Fl_Group.
Reimplemented in Fl_Gl_Window, and Fl_Glut_Window.
◆ hide()
|
virtual |
Removes the window from the screen.
If the window is already hidden or has not been shown then this does nothing and is harmless.
Reimplemented from Fl_Widget.
Reimplemented in Fl_Double_Window, Fl_Gl_Window, Fl_Menu_Window, and Fl_Overlay_Window.
◆ hotspot()
| void Fl_Window::hotspot | ( | int | x, |
| int | y, | ||
| int | offscreen = 0 ) |
Positions the window so that the mouse is pointing at the given position, or at the center of the given widget, which may be the window itself.
If the optional offscreen parameter is non-zero, then the window is allowed to extend off the screen (this does not work with some X window managers).
- See also
- position()
◆ icon() [1/3]
| const void * Fl_Window::icon | ( | ) | const |
Gets the current icon window target dependent data.
- Deprecated
- in 1.3.3
◆ icon() [2/3]
| void Fl_Window::icon | ( | const Fl_RGB_Image * | icon | ) |
Sets or resets a single window icon.
A window icon can be changed while the window is shown, but this may be platform and/or window manager dependent. To be sure that the window displays the correct window icon you should always set the icon before the window is shown.
If a window icon has not been set for a particular window, then the default window icon (see links below) or the system default icon will be used.
- Parameters
-
[in] icon icon for this window, NULL to reset window icon.
◆ icon() [3/3]
| void Fl_Window::icon | ( | const void * | ic | ) |
Sets the current icon window target dependent data.
- Deprecated
- in 1.3.3
◆ iconize()
| void Fl_Window::iconize | ( | ) |
Iconifies the window.
If you call this when shown() is false it will show() it as an icon. If the window is already iconified this does nothing.
Call show() to restore the window.
When a window is iconified/restored (either by these calls or by the user) the handle() method is called with FL_HIDE and FL_SHOW events and visible() is turned on and off.
There is no way to control what is drawn in the icon except with the string passed to Fl_Window::xclass(). You should not rely on window managers displaying the icons.
◆ icons()
| void Fl_Window::icons | ( | const Fl_RGB_Image * | icons[], |
| int | count ) |
Sets the window icons.
You may set multiple window icons with different sizes. Dependent on the platform and system settings the best (or the first) icon will be chosen.
The given images in icons are copied. You can use a local variable or free the images immediately after this call.
If count is zero, current icons are removed. If count is greater than zero (must not be negative), then icons[] must contain at least count valid image pointers (not NULL). Otherwise the behavior is undefined.
- Parameters
-
[in] icons icons for this window [in] count number of images in icons. Set to 0 to remove the current icons
◆ make_current()
| void Fl_Window::make_current | ( | ) |
Sets things up so that the drawing functions in <FL/fl_draw.H> will go into this window.
This is useful for incremental update of windows, such as in an idle callback, which will make your program behave much better if it draws a slow graphic. Danger: incremental update is very hard to debug and maintain!
This method only works for the Fl_Window and Fl_Gl_Window derived classes.
◆ modal()
|
inline |
Returns true if this window is modal.
◆ resize()
|
virtual |
Changes the size and position of the window.
If shown() is true, these changes are communicated to the window server (which may refuse that size and cause a further resize). If shown() is false, the size and position are used when show() is called. See Fl_Group for the effect of resizing on the child widgets.
You can also call the Fl_Widget methods size(x,y) and position(w,h), which are inline wrappers for this virtual function.
A top-level window can not force, but merely suggest a position and size to the operating system. The window manager may not be willing or able to display a window at the desired position or with the given dimensions. It is up to the application developer to verify window parameters after the resize request.
Reimplemented from Fl_Group.
Reimplemented in Fl_Double_Window, Fl_Gl_Window, and Fl_Overlay_Window.
◆ set_menu_window()
|
inline |
Marks the window as a menu window.
This is intended for internal use, but it can also be used if you write your own menu handling. However, this is not recommended.
This flag is used for correct "parenting" of windows in communication with the windowing system. Modern X window managers can use different flags to distinguish menu and tooltip windows from normal windows.
This must be called before the window is shown and cannot be changed later.
◆ set_modal()
|
inline |
A "modal" window, when shown(), will prevent any events from being delivered to other windows in the same program, and will also remain on top of the other windows (if the X window manager supports the "transient for" property).
Several modal windows may be shown at once, in which case only the last one shown gets events. You can see which window (if any) is modal by calling Fl::modal().
◆ set_non_modal()
|
inline |
A "non-modal" window (terminology borrowed from Microsoft Windows) acts like a modal() one in that it remains on top, but it has no effect on event delivery.
There are three states for a window: modal, non-modal, and normal.
◆ set_tooltip_window()
|
inline |
Marks the window as a tooltip window.
This is intended for internal use, but it can also be used if you write your own tooltip handling. However, this is not recommended.
This flag is used for correct "parenting" of windows in communication with the windowing system. Modern X window managers can use different flags to distinguish menu and tooltip windows from normal windows.
This must be called before the window is shown and cannot be changed later.
- Note
- Since Fl_Tooltip_Window is derived from Fl_Menu_Window, this also clears the menu_window() state.
◆ shape() [1/2]
|
inline |
Set the window's shape with an Fl_Image.
- See also
- void shape(const Fl_Image* img)
◆ shape() [2/2]
| void Fl_Window::shape | ( | const Fl_Image * | img | ) |
Assigns a non-rectangular shape to the window.
This function gives an arbitrary shape (not just a rectangular region) to an Fl_Window. An Fl_Image of any dimension can be used as mask; it is rescaled to the window's dimension as needed.
The layout and widgets inside are unaware of the mask shape, and most will act as though the window's rectangular bounding box is available to them. It is up to you to make sure they adhere to the bounds of their masking shape.
The img argument can be an Fl_Bitmap, Fl_Pixmap, Fl_RGB_Image or Fl_Shared_Image:
- With Fl_Bitmap or Fl_Pixmap, the shaped window covers the image part where bitmap bits equal one, or where the pixmap is not fully transparent.
- With an Fl_RGB_Image with an alpha channel (depths 2 or 4), the shaped window covers the image part that is not fully transparent.
- With an Fl_RGB_Image of depth 1 (gray-scale) or 3 (RGB), the shaped window covers the non-black image part.
- With an Fl_Shared_Image, the shape is determined by rules above applied to the underlying image. The shared image should not have been scaled through Fl_Shared_Image::scale().
Platform details:
- On the unix/linux platform, the SHAPE extension of the X server is required. This function does control the shape of Fl_Gl_Window instances.
- On the MSWindows platform, this function does nothing with class Fl_Gl_Window.
- On the Mac platform, OS version 10.4 or above is required. An 8-bit shape-mask is used when
imgis an Fl_RGB_Image: with depths 2 or 4, the image alpha channel becomes the shape mask such that areas with alpha = 0 are out of the shaped window; with depths 1 or 3, white and black are in and out of the shaped window, respectively, and other colors give intermediate masking scores. This function does nothing with class Fl_Gl_Window.
The window borders and caption created by the window system are turned off by default. They can be re-enabled by calling Fl_Window::border(1).
A usage example is found at example/shapedwindow.cxx.
- Version
- 1.3.3 (and requires compilation with FLTK_ABI_VERSION >= 10303)
◆ show() [1/2]
|
virtual |
Puts the window on the screen.
Usually (on X) this has the side effect of opening the display.
If the window is already shown then it is restored and raised to the top. This is really convenient because your program can call show() at any time, even if the window is already up. It also means that show() serves the purpose of raise() in other toolkits.
Fl_Window::show(int argc, char **argv) is used for top-level windows and allows standard arguments to be parsed from the command-line.
- Note
- For some obscure reasons Fl_Window::show() resets the current group by calling Fl_Group::current(0). The comments in the code say "get rid of very common user bug: forgot end()". Although this is true it may have unwanted side effects if you show() an unrelated window (maybe for an error message or warning) while building a window or any other group widget.
- Todo
- Check if we can remove resetting the current group in a later FLTK version (after 1.3.x). This may break "already broken" programs though if they rely on this "feature".
Reimplemented from Fl_Widget.
Reimplemented in Fl_Double_Window, Fl_Gl_Window, Fl_Menu_Window, Fl_Overlay_Window, and Fl_Single_Window.
◆ show() [2/2]
| void Fl_Window::show | ( | int | argc, |
| char ** | argv ) |
Puts the window on the screen and parses command-line arguments.
Usually (on X) this has the side effect of opening the display.
This form should be used for top-level windows, at least for the first (main) window. It allows standard arguments to be parsed from the command-line. You can use argc and argv from main(int argc, char **argv) for this call.
The first call also sets up some system-specific internal variables like the system colors.
- Todo
- explain which system parameters are set up.
- Parameters
-
argc command-line argument count, usually from main() argv command-line argument vector, usually from main()
- See also
- virtual void Fl_Window::show()
◆ shown()
|
inline |
◆ size_range()
|
inline |
Sets the allowable range the user can resize this window to.
This only works for top-level windows.
-
minwandminhare the smallest the window can be. Either value must be greater than 0. -
maxwandmaxhare the largest the window can be. If either is equal to the minimum then you cannot resize in that direction. If either is zero then FLTK picks a maximum size in that direction such that the window will fill the screen. -
dwanddhare size increments. The window will be constrained to widths of minw + N * dw, where N is any non-negative integer. If these are less or equal to 1 they are ignored (this is ignored on WIN32). -
aspectis a flag that indicates that the window should preserve its aspect ratio. This only works if both the maximum and minimum have the same aspect ratio (ignored on WIN32 and by many X window managers).
If this function is not called, FLTK tries to figure out the range from the setting of resizable():
- If resizable() is NULL (this is the default) then the window cannot be resized and the resize border and max-size control will not be displayed for the window.
- If either dimension of resizable() is less than 100, then that is considered the minimum size. Otherwise the resizable() has a minimum size of 100.
- If either dimension of resizable() is zero, then that is also the maximum size (so the window cannot resize in that direction).
It is undefined what happens if the current size does not fit in the constraints passed to size_range().
◆ wait_for_expose()
| void Fl_Window::wait_for_expose | ( | ) |
Waits for the window to be displayed after calling show().
Fl_Window::show() is not guaranteed to show and draw the window on all platforms immediately. Instead this is done in the background; particularly on X11 it will take a few messages (client server roundtrips) to display the window. Usually this small delay doesn't matter, but in some cases you may want to have the window instantiated and displayed synchronously.
Currently (as of FLTK 1.3.4) this method has an effect on X11 and Mac OS. On Windows, show() is always synchronous. The effect of show() varies with versions of Mac OS X: early versions have the window appear on the screen when show() returns, later versions don't. If you want to write portable code and need this synchronous show() feature, add win->wait_for_expose() on all platforms, and FLTK will just do the right thing.
This method can be used for displaying splash screens before calling Fl::run() or for having exact control over which window has the focus after calling show().
If the window is not shown(), this method does nothing.
- Note
- Depending on the platform and window manager wait_for_expose() may not guarantee that the window is fully drawn when it is called. Under X11 it may only make sure that the window is mapped, i.e. the internal (OS dependent) window object was created (and maybe shown on the desktop as an empty frame or something like that). You may need to call Fl::flush() after wait_for_expose() to make sure the window and all its widgets are drawn and thus visible.
- FLTK does the best it can do to make sure that all widgets get drawn if you call wait_for_expose() and Fl::flush(). However, dependent on the window manager it can not be guaranteed that this does always happen synchronously. The only guaranteed behavior that all widgets are eventually drawn is if the FLTK event loop is run continuously, for instance with Fl::run().
- See also
- virtual void Fl_Window::show()
Example code for displaying a window before calling Fl::run()
Note that the window will not be responsive until the event loop is started with Fl::run().
◆ xclass() [1/2]
| const char * Fl_Window::xclass | ( | ) | const |
Returns the xclass for this window, or a default.
◆ xclass() [2/2]
| void Fl_Window::xclass | ( | const char * | xc | ) |
Sets the xclass for this window.
A string used to tell the system what type of window this is. Mostly this identifies the picture to draw in the icon. This only works if called before calling show().
Under X, this is turned into a XA_WM_CLASS pair by truncating at the first non-alphanumeric character and capitalizing the first character, and the second one if the first is 'x'. Thus "foo" turns into "foo, Foo", and "xprog.1" turns into "xprog, XProg".
Under Microsoft Windows, this string is used as the name of the WNDCLASS structure, though it is not clear if this can have any visible effect.
- Since
- FLTK 1.3 the passed string is copied. You can use a local variable or free the string immediately after this call. Note that FLTK 1.1 stores the pointer without copying the string.
If the default xclass has not yet been set, this also sets the default xclass for all windows created subsequently.
Member Data Documentation
◆ current_
|
staticprotected |
Stores the last window that was made current.
See current() const
The documentation for this class was generated from the following files:
- Fl_Window.H
- Fl.cxx
- Fl_arg.cxx
- fl_cursor.cxx
- Fl_Window.cxx
- Fl_Window_fullscreen.cxx
- Fl_Window_hotspot.cxx
- Fl_Window_iconize.cxx
- Fl_Window_shape.cxx